Conditions associated with Acute pain
Post Surgical Pains: Pain serves a biological function. It signals the presence of damage or disease within the body. In the case of postoperative pain it is the result of the surgery
Pain serves a biological function. It signals the presence of damage or disease within the body. In the case of postoperative pain it is the result of the surgery
FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR POST OPERATIVE PAINS
- Clinical Factors
- Patient Related Factors
- Local Factors
RENAL COLIC :- Pain commonly caused by kidney stones. The pain typically begins in the loin (The loins are the sides between the lower ribs and pelvis) region and often radiates to the hypochondrium (The hypochondrium is the upper part of the abdomen caudal to the lowest ribs of the thorax).
TRAUMATIC PAINS :- Pains occurs after the different injuries and trauma.
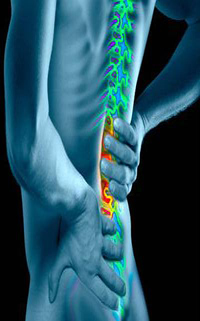
ACUTE LOW BACK PAIN :- is a common musculo-skeletal disorder affecting 80% of people at some point in their lives . It can be either acute, sub-acute or chronic in duration. Causes of lower back pain are varied like sprain or strain in the muscles and soft tissues of the back.
Starting at the top, the spine has four regions:
The lumbar region of the back, where most back pain is felt, supports the weight of the upper body.
Causes Lower Back Pain
- With Age, bone strength , muscle elasticity and tone tend to decreases. The discs begin to lose fluid and flexibility, which decreases their ability to cushion the vertebrae.
- Pain can occur when, someone lifts something too heavy or over stretches, causing a sprain, strain, or spasm in one of the muscles or ligaments in the back. If the spine becomes overly strained or compressed, a disc may rupture or bulge outward. This rupture may put pressure on one of the more than 50 nerves rooted to the spinal cord thatcontrol body movements and transmit signals from the body to the brain. When these nerve roots become compressed or irritated then back pain occurs
SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS & POST SURGICAL FIBROSIS :-All incisions produce scarring, which consists of a repair process by which the cut tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue. Postoperative fibrosis, corresponds to secondary surgical scarring, but the term may be referred to those cases where excessive scarring is present, that is, the formation of more fibrous tissue than needed. If after a spinal operation this excessive scarring compresses a nerve, it elicits intense pain & it is responsible for “FAILURE SPINAL SURGERY SYNDROM”
by fibrous tissue. Postoperative fibrosis, corresponds to secondary surgical scarring, but the term may be referred to those cases where excessive scarring is present, that is, the formation of more fibrous tissue than needed. If after a spinal operation this excessive scarring compresses a nerve, it elicits intense pain & it is responsible for “FAILURE SPINAL SURGERY SYNDROM”
Failed Spinal surgery syndrome or post-laminectomy syndrome is a condition characterized by persistent pain following back surgeries. Contributing factors include recurrent disc herniation, persistent post-operative pressure on a spinal nerve, altered joint mobility, joint hyper-mobility with instability, scar tissue (fibrosis), depression, anxiety, sleeplessness and spinal muscular deconditioning
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) as a central cause of inflammatory spinal pain
- Surgical adhesions are a common and often severe complication of abdominal or pelvic injury that cause pelvic pain, bowel obstruction, and infertility in women
It is accepted that the major risk factors to develop postoperative fibrosis depend on:
- The scar :- The greater the surgical wound extension and bleeding, the greater the risk for developing fibrosis
- The patient :- Some individuals have a spontaneous tendency to scar more than needed; even little skin cuts give rise to excessive scarring
CANCER PAINS :- The International Association for the Study of Pain says it is “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience in association with actual or  potential tissue damage, pain is a sensation that hurts, and it has both physical and emotional aspects to consider Pain, which can be caused by the disease itself or by treatments, is common in people with cancer, although not all people with cancer will experience pain.
potential tissue damage, pain is a sensation that hurts, and it has both physical and emotional aspects to consider Pain, which can be caused by the disease itself or by treatments, is common in people with cancer, although not all people with cancer will experience pain.
Approximately 30% to 50% of people with cancer experience pain while undergoing treatment and 70% to 90% of people with advanced cancer experience pain