OVERDOSE
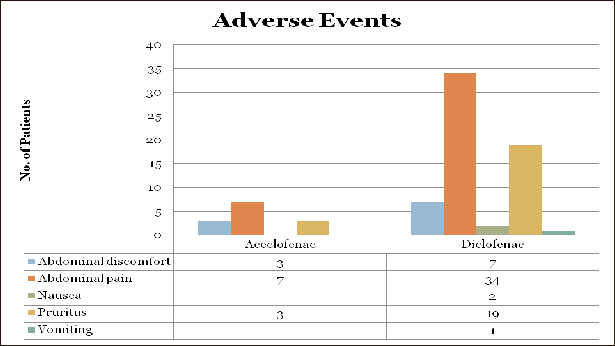
Overdosage may cause nausea, vomiting, pain abdomen, dizziness, somnolence, headache, sweating, pancreatitis, hepatic failure and acute renal failure. Management of acute poisoning with NSAIDS essentially consists of supportive and symptomatic measures. There are no human data available on the consequence of Aceclofenac overdosage. Supportive and symptomatic treatment should be given for other complications.
PRECAUTIONS
Patients with a history of hypertension, established ischemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and/or cerebrovascular disease should be appropriately monitored and treated with Aceclofenac controlled release injection only after careful consideration, as fluid retention and edema have been reported in association with NSAID therapy.
RENAL
Patients with renal, cardiac or hepatic impairment and the elderly should be kept under surveillance, since the use of NSAIDs may result in deterioration of renal function. The importance of prostaglandins in maintaining renal blood flow should be taken into account in patients with impaired cardiac or renal function, those being treated with diuretics or recovering from major surgery. Effects on renal function are usually reversible on withdrawal of Aceclofenac.
RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
Use of Aceclofenac controlled release injection is contraindicated in patients with a history of asthma.
HEPATIC
If abnormal liver function tests persist or worsen, clinical signs or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop or if other manifestations occur (eosinophilia, rash), Aceclofenac controlled release injection injection should be discontinued. Hepatitis may occur without prodromal symptoms. Use of Aceclofenac injection in patients with hepatic porphyria may trigger an attack.
HAEMATOLOGICA EFFECT
Aceclofenac controlled release injection may reversibly inhibit platelet aggregation. Patients with defects of haemostasis, bleeding diathesis or haematological abnormalities should be carefully monitored.
ELDERLY
The elderly are at increased risk of the consequences of adverse reactions. Caution is required in patients with a history of heart failure or hypertension. The elderly have an increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation which may be fatal.
IMPAIRED FEMAL FERTILITY
The use of Aceclofenac controlled release injection may impair female fertility and is not recommended in women attempting to conceive. In women who have difficulties conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility, withdrawal of Aceclofenac injection should be considered.
DERMATOLOGICAL
Serious skin reactions are very rarely observed with the use of NSAIDs. Patients appear to be at highest risk for these reactions early in the course of therapy: the onset of the reaction occurring in the majority of cases within the first month of treatment. Aceclofenac should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
WARNINGS
Close medical surveillance is imperative in patients with symptoms indicative of gastrointestinal disorders, with a history suggestive of gastro-intestinal ulceration, with ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, bleeding diathesis or haematological abnormalities.
Caution should be advised in patients receiving concomitant medications which could increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, selective serotonin-re uptake inhibitors and anti-platelet agents. Concomitant use of anticoagulants with intramuscular Aceclofenac is contraindicated. GI bleeding or ulceration occurs in patients receiving Aceclofenac, the treatment should be withdrawn.
Close medical surveillance is also imperative in patients suffering from severe impairment of hepatic function.
There is no information on the use of Aceclofenac during pregnancy. Aceclofenac should not be administered during pregnancy, unless there are compelling reasons for doing so. The lowest effective dose should be administered.
Same is the case in Lactation, The use of Aceclofenac has to be avoided unless the potential benefits to the mother outweigh the possible risks to the children.
As with other NSAIDs, allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions, can also occur without earlier exposure to the drug.
Aceclofenac controlled release injection should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
A total of 300 patients were randomly attributed assigned to receive either Aceclofenac (150 patients) or Diclofenac (150 patients). Both groups showed improvement on VAS for pain at rest at the end of 30 minutes, 1, 2, 4, 8, 24 and 48 hours after treatment (Table 1). Aceclofenac showed a quantitatively better improvement in the change in mean VAS score from baseline at all points of measurement. This improvement became statistically in favor of Aceclofenac group at all points of assessment (p<0.05).
| Table 1: Changes in mean VAS score from baseline | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | 30 min | 1 hr | 2 hr | 4 hr | 8 hr | 24 hr | 48 hr |
| Aceclofenac (n=150) | |||||||
| Mean | 13.37 | 21.35 | 29.42 | 37.12 | 43.06 | 49.46 | 55.77 |
| SD | 6.91 | 7.89 | 9.01 | 1016 | 10.40 | 10.14 | 8.79 |
| Diclofenac (n=150) | |||||||
| Mean | 11.06 | 19.06 | 27.78 | 36.50 | 42.10 | 48.00 | 52.95 |
| SD | 4.57 | 6.21 | 7.20 | 7.37 | 8.70 | 9.92 | 11.33 |
| t-test p value | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 |
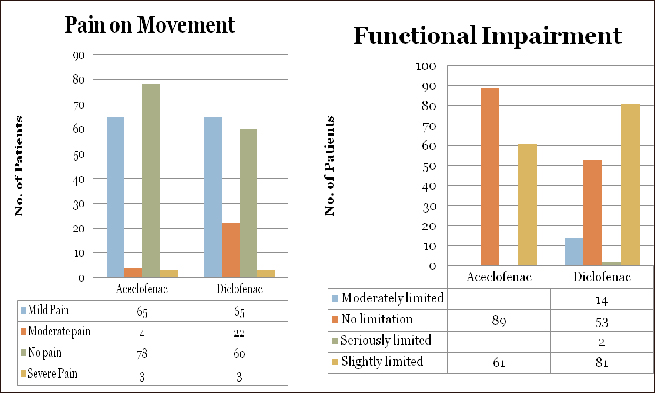
The modified Schober’s test showed progressive improvements at 8 hrs, 24 hrs and after 48 hrs of treatment in both groups, but the improvement was higher and significant in the Aceclofenac group than in the Diclofenac at 8 hrs, 24 hrs and after 48 hrs of treatment (Table 2).
| Table 2: Changes in mean Schober’s test value from baseline | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 hr | 24 hr | 48 hr | |
| Aceclofenac (n=150) | |||
| Mean | -0.061 | -1.09 | -2.36 |
| SD | 0.34 | 0.50 | 5.70 |
| Diclofenac (n=150) | |||
| Mean | -0.47 | -0.87 | -1.36 |
| SD | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.75 |
| t-test p value | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 |
Registration No. -CCT NAPN 15395